Published on: February 14, 2024
Author: Admin
Many people mistakenly believe that PCOD and PCOS are the same, as both conditions involve hormonal imbalances and affect the ovaries. However, there are key differences between them.
During a typical menstrual cycle, a woman’s ovaries release a mature egg approximately two weeks after her period, a process known as ovulation. The ovaries also produce essential hormones that regulate fertility, control the menstrual cycle, and impact overall reproductive health.
Since PCOD and PCOS share similar symptoms, they are often confused. Understanding these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the difference between PCOD and PCOS!
Understanding PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a medical condition caused by an endocrine disorder among women. This causes the increased production of male hormones in ovaries, interfering with their ability to produce eggs naturally. The condition is developed during their reproductive age.
Irregular menstrual cycle, hair growth in the face and body, and obesity are some of the most common symptoms of this medical condition.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) typically affects the ovaries by forming fluids in a saclike structure with immature eggs. These cysts are developed around the ovaries. If untreated, women with PCOS are at increased risk of developing certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and infertility.
Understanding PCOD
PCOD is a medical condition caused by mild hormonal imbalances among women. The condition is developed during their reproductive age. The full form of PCOD is polycystic ovarian deficiency. Irregular menstrual cycle, hair growth in the face and body, and obesity are some of the most common symptoms of this medical condition.
Polycystic ovarian deficiency (PCOD) is caused by ovaries that produce immature eggs. This leads to the formation of cysts. These cysts are developed around the ovaries, making them look swollen.
This medical condition can be treated easily with a healthy lifestyle. PCOD is not a severe condition like PCOS. However, if untreated, women with PCOD are at an increased risk of developing certain medical conditions such as miscarriage, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, and so on.
Causes of PCOD and PCOS
The exact reasons for the condition are still unknown. However, experts believe that PCOS and PCOD problems in females are associated with increased production of male hormones in their bodies. This interferes with their ability to produce eggs naturally from ovaries.
Other factors of this medical condition involve genes, inflammation, and insulin resistance. All these factors are associated with the excess production of the male hormone androgens.
Genes
PCOS and PCOD are hereditary medical conditions. The meaning of PCOD and PCOS is likely to pass through the generations or family members such as grandmother, mother, and siblings.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is the disorder by which the cells become more resistant towards the insulin prepared by the pancreas.
Insulin is the hormone secreted by the pancreas to help the body with blood sugar regulation and digestion. Insulin helps to convert the sugar into energy from the consumed food.
When cells become more resistant towards insulin, the demand for more insulin is increased by the body. Hence, the pancreas tends to produce additional insulin to compensate for the need. This results in the production of male hormones by the ovaries, such as androgens. Androgen secretion leads to developing immature eggs from the ovaries and controls ovulation – resulting in infertility and obesity.
Inflammation
Women with this medical condition tend to have increased levels of chronic low-grade inflammation in their bodies. Your physician may measure these levels by blood tests, which examine the levels of white blood cells and C-reactive protein (CRP). These examinations indicate the level of excess inflammation in women’s bodies.
Common Symptoms of PCOD and PCOS
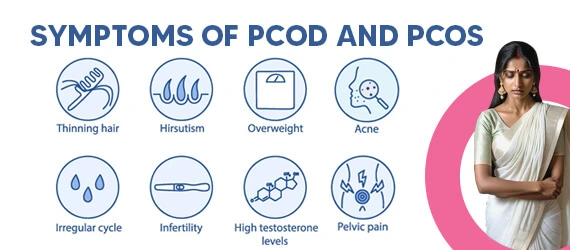
Some women with PCOD or PCOS can typically begin to see the symptoms from their very first menstrual cycle.
Whereas others begin to notice the condition only when they go through severe complications, such as infertility. Though, it is still misunderstood by many people for the different between pcos and pcod.
The most common pcos and pcod symptoms include:
Irregular Menstrual Cycle
The insufficient discharge of eggs from ovaries prevents the monthly shedding of the uterine lining. This causes an irregular menstrual cycle.
Heavy Bleeding
Since the monthly shedding from the uterine lining builds up for a prolonged period, it causes heavy bleeding during the menstruation cycle.
Hair Growth
Studies show that due to this medical condition, more than 70% of women grow hair on their face, chest, abdomen, arms, legs, and back. Excessive hair growth in women like men is referred to as hirsutism.
Acne
The increased production of male hormones in women causes them to develop acne on their face, chest, and back.
Obesity
One of the common symptoms of PCOD problem in females is gaining weight abruptly. This causes them to struggle to do their routine and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Hyperpigmentation
The darkening of the skin is referred to as hyperpigmentation. Women with the condition develop dark patches around their necks, between their legs, armpits, and under their breasts.
Baldness
Some women with the condition may lose hair in patches on their scalp causing them to bald like men.
Skin Tags
Skin tags are tumours that look like extra loose skin. These skin tags don’t cause any pain and are harmless. Usually, they grow around the neck and armpits.
Infertility
PCOD and PCOS are significant factors of infertility in women. The inability to ovulate regularly makes it difficult to get pregnant.
Headache
Some women with the condition experience frequent headaches due to the hormonal changes.
Difference Between PCOD and PCOS
For a better understanding of PCOD vs PCOS, the table below highlights the key differences between these two medical conditions. This comparison will help you distinguish their symptoms, causes, and effects on reproductive health.
| PCOD | PCOS |
|---|---|
| PCOD is an ovarian disorder. | PCOS is an endocrine disorder. |
| It is a common disorder. | It is a serious medical condition. |
| Ovarian cysts are developed by immature eggs. | Hormonal imbalance that affects metabolism. |
| Symptoms include irregular or absent periods, acne, and obesity. | Symptoms include irregular or absent periods, acne, obesity, and excessive hair growth. |
| Requires lifestyle changes and medications to regulate the menstrual cycle. | Requires lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, and medications to improve insulin resistance. |
| PCOD doesn’t have any serious complications. | PCOS has a higher risk of cardiac conditions, diabetes, obesity, and endometrial cancer. |
| The medical condition can be managed with lifestyle changes. | The condition affects the endocrine system and usually requires external hormone intake. |
| With PCOD, a woman can get pregnant with little medical help and lifestyle changes. | With PCOS, women usually find it difficult to get pregnant and are at an increased risk of miscarriages. |
Diagnosis of PCOD and PCOS
After having a complete analysis of your medical history and symptoms, the gynaecologist will examine your pelvis and reproductive organs and suggest the best procedure for your condition.
Tests Included in the Diagnosis:
- Ultrasound: The test is used to analyze the size of the ovaries and examine if the ovaries have any cysts. It can also determine the thickness of the endometrium, which is the lining of the uterus.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests check the glucose, triglyceride, and cholesterol levels in the blood. In addition, the levels of androgen and other hormones are also measured.
Treatment of PCOD and PCOS
The treatment of PCOD and PCOS is based on various reasons such as symptoms, age, the desire to get pregnant or not, and so on.
If a woman desires to get pregnant, the treatment options may include:
Change in Lifestyle
Regular physical activity and a healthy diet play a major role in improving overall health. A lifestyle change can help women regulate insulin levels in the blood and also help with regular ovulation.
Medication to Induce Ovulation
Ovulation is the primary cause of pregnancy. If a woman desires to get pregnant, certain drugs prescribed by your gynaecologist are helpful to induce ovulation even with PCOS or PCOD.
Surgery
The recommended surgery for PCOS is known as laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD). The surgery is performed to remove cells that produce male hormones (androgens) from the ovaries. This process helps in restoring ovulation. However, surgeons rarely suggest this option as there are the latest medications available to treat the condition more effectively, even without surgery.
IVF
Couples opt for this option when pills don’t help them with conception or induce ovulation. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the procedure performed to conceive outside the body by fertilizing sperm and eggs in a laboratory setting. Once the embryos are formed, they are later transferred into the woman’s uterus.
If a woman does not desire to get pregnant, the treatment options may include:
Hormonal Birth Control
Birth control options help women balance normal hormones, regulate ovulation, regulate the menstrual cycle, protect from endometrial cancer, help with hirsutism, and improve acne. The hormonal birth control options come in patches, pills, shots, intrauterine devices (IUD), and vaginal rings.
Insulin-Sensitizing Medicine
Medications like metformin help treat women with type 2 diabetes. It helps regulate insulin levels in the blood, which leads to normalizing the menstrual cycle in women. The medication is also helpful for weight loss.
Medications to Block Androgens
Some medications work well in blocking the production of male hormones (androgens) in women. This helps to control hirsutism, which is the condition of excessive hair growth on the face and body of the woman. This also helps to control acne on the face and buttocks.
Complications of PCOD and PCOS
Before knowing the complications of PCOD and PCOS, understanding the problems associated with these conditions is essential.
PCOS and PCOD are common medical conditions in women that affect the heart, insulin levels in the blood, reproductive system, and contribute to obesity.
Common Complications of PCOD and PCOS
- Recurrent pregnancy loss.
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
- Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Hypertension or high blood pressure during pregnancy or delivery.
- Unusual growth of the baby during pregnancy.
- Increased risk of premature birth.
- Endometrial hyperplasia, a precancerous medical condition.
- Higher possibility of developing uterine cancer.
Summary
The answer to the question "Are PCOS and PCOD the same?" is no, they are not the same. Even though most people interchange these terms, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose the condition and provide appropriate treatment for better outcomes.
Note: Medications should only be taken when prescribed by a reputed gynaecologist.